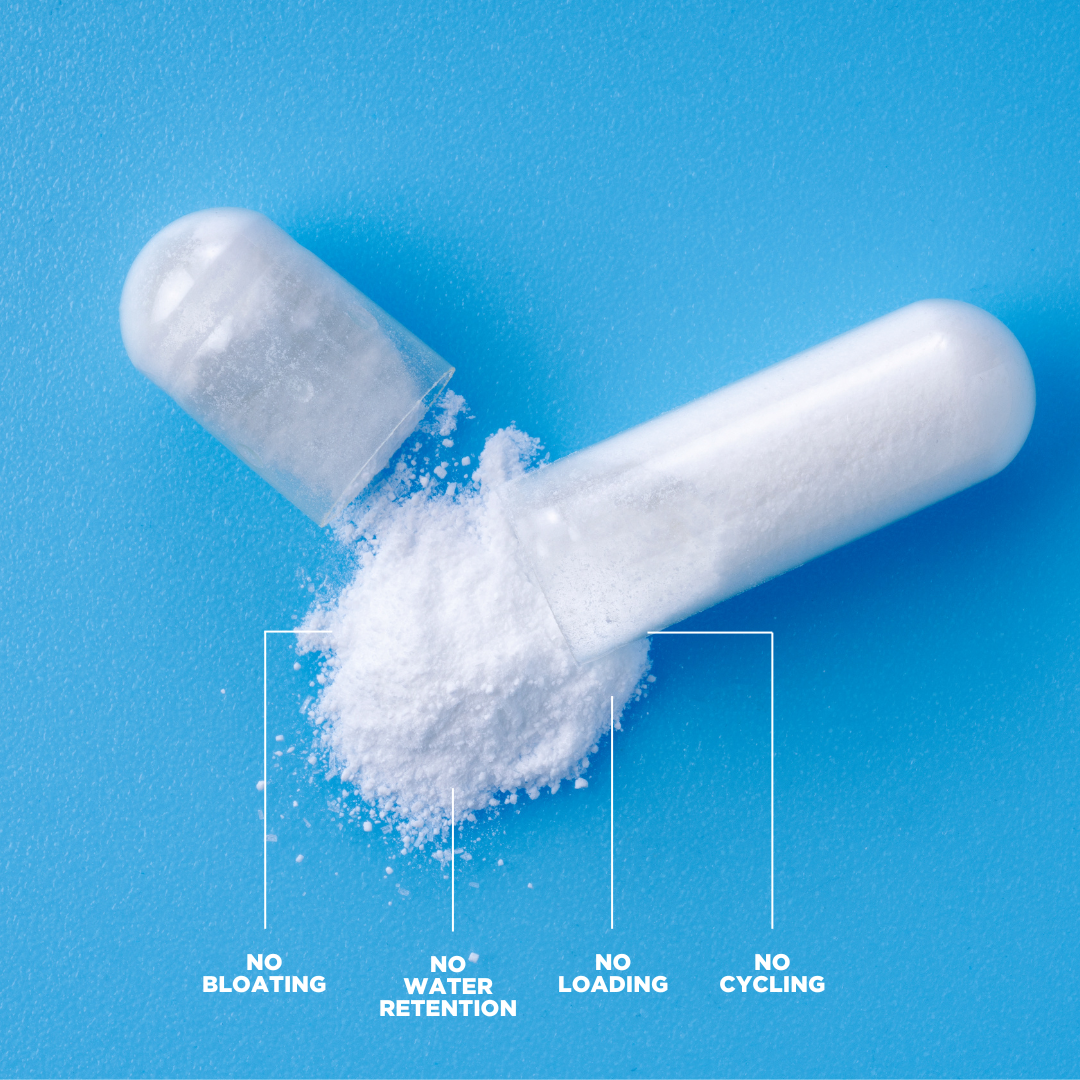
When it comes to overall wellness, Creatine HCl is somewhat of a hidden gem that’s ready to unleash its potential within your body. As a leading producer of Creatine HCl supplements, CON-CRĒT is here to shed light on this intriguing compound. We’ll be talking about what kind of timeline you can expect if you add creatine HCl to your daily routine.
What Is Creatine HCl?
Creatine HCl, short for creatine hydrochloride, is a version of creatine that’s been bound with a hydrochloride salt molecule. This is different from the more commonly consumed creatine monohydrate, which is bound with a water molecule instead.
This difference in molecular structure impacts how your body processes the supplement. Creatine HCl is more soluble, which means it dissolves more easily in fluids, leading to better absorption in the body. This improved absorption rate can lead to fewer side effects, such as bloating and stomach discomfort, that are often associated with creatine monohydrate.

At CON-CRĒT, our Creatine HCl supplements are formulated with this science in mind. We aim to deliver a product that supports your workout performance and fits comfortably into your wellness routine. Our creatine HCl supplements aim to maximize the benefits of creatine while minimizing potential side effects.
How Does Creatine HCl Work in the Body?
Upon ingestion, Creatine HCl gets absorbed into your bloodstream from the intestines. Due to its high solubility, this process is much more efficient compared to creatine monohydrate. Once in the bloodstream, it's transported to various parts of the body, including the brain and muscle tissues.
In the muscles, creatine plays a crucial role in energy production. It boosts the synthesis of phosphocreatine (PCr), a high-energy molecule that supports the production of ATP — the primary energy currency of cells. This increase in ATP availability is especially beneficial during high-intensity, short-duration exercises like weightlifting or sprinting, where ATP demand is high.
However, the benefits of Creatine HCl aren't restricted to muscle tissues. Creatine can also support brain function. The brain, like muscles, requires a significant amount of energy, and creatine can help meet this demand.
When Can You Start Seeing Results from Creatine HCl?
The exact timeline can vary from person to person, but users can generally start noticing the benefits of Creatine HCl within a week or two of regular use. You may notice you’re maintaining muscle mass and optimal energy, and you might find that you can push a little harder in your workouts.
However, there are a few factors that can play a role in speeding up or slowing down your progress, such as:
- Dosage: The amount of Creatine HCl you take can affect how quickly you see results. Higher doses may yield quicker results, but it's always best to follow recommended dosage guidelines to ensure safe and effective use.
- Frequency of Use: Consistency is key when it comes to supplementing with Creatine HCl. Regular usage can lead to more noticeable results over time as your body's creatine stores become fully saturated.
- Metabolism: Everyone's body processes substances at different rates. If you have a faster metabolism, you may absorb and utilize Creatine HCl more quickly than someone with a slower metabolism.
- Diet: A well-balanced diet can influence the effectiveness of Creatine HCl. Consuming a diet rich in proteins and carbs can provide the necessary building blocks to support creatine synthesis.
- Hydration: Creatine works best when your body is well-hydrated. Staying adequately hydrated can help ensure your body efficiently absorbs and utilizes Creatine HCl.
- Exercise Routine: The effects of Creatine HCl can be more pronounced if you're regularly engaging in high-intensity workouts. This is due to creatine's role in energy production during these types of activities.
- Quality: Not all Creatine HCl supplements are created equal. The quality of the supplement can impact its effectiveness and the speed at which you see results, so make sure that you’re only using the very best.
- Age: Age can influence the body's ability to absorb and utilize creatine. Younger individuals may see results more quickly due to their naturally higher metabolism and muscle mass.
- Body Mass: Your body mass can also affect how quickly you see results from Creatine HCl. Individuals with a higher body weight may require a higher dosage to see the same effects as someone with less body mass.
Are There Any Side Effects to Taking Creatine HCl?
Before starting any new wellness routine, it's important to understand the potential side effects. Creatine HCl, despite being a supercharged supplement, is no different. However, the good news is that Creatine HCl is generally well-tolerated and is considered safe for most people.

Some users might experience minor digestive discomfort, but this is typically linked to high dosage or insufficient water intake. Remember, hydration is key when taking creatine! Other potential side effects may include muscle cramping, but this is far less common with Creatine HCl than with creatine monohydrate.
The Power of Patience With Creatine HCl
If there's one thing to remember from this discussion, it's this: Patience is key when it comes to Creatine HCl. We know expecting immediate, dramatic results can be tempting, but real and lasting progress takes time.
So, keep going, stay consistent, and let Creatine HCl work its magic in your body. Regular usage, combined with a balanced diet, adequate hydration, and a consistent workout routine, can help you unlock the full potential of Creatine HCl.
Are you ready to give Creatine HCl a try? We invite you to explore our range of Creatine HCl products at CON-CRĒT. Whether you're a gym-goer, an athlete, a bodybuilder, or someone simply focused on overall wellness, adding our Creatine HCl to your routine can help boost your workouts and overall health.
Sources:
Role of the Phosphocreatine System on Energetic Homeostasis in Skeletal and Cardiac Muscles | PMC
Pharmacokinetics of the Dietary Supplement Creatine | NIH
Physiology, Adenosine Triphosphate | NCBI Bookshelf
The Differences and Similarities Between Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins | livestrong